Unlocking the Power of Liquid Vacuum Pumps: A Deep Dive into their Working Principles

Ever wondered how some industrial processes achieve incredibly low pressures? The answer often lies in the ingenious operation of liquid vacuum pumps. These unsung heroes of various industries, from chemical processing to power generation, harness the power of liquids to create vacuums essential for a multitude of applications. Let's delve into the fascinating mechanics behind the liquid vacuum pump working principle.
Liquid vacuum pumps, unlike their dry counterparts, utilize a liquid medium, often water or oil, to achieve vacuum conditions. This liquid plays a crucial role in capturing and expelling gas molecules, effectively lowering the pressure within a sealed system. Understanding how these pumps function is key to optimizing their performance and selecting the right pump for a specific application. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the liquid vacuum pump working principle and explore its diverse applications.
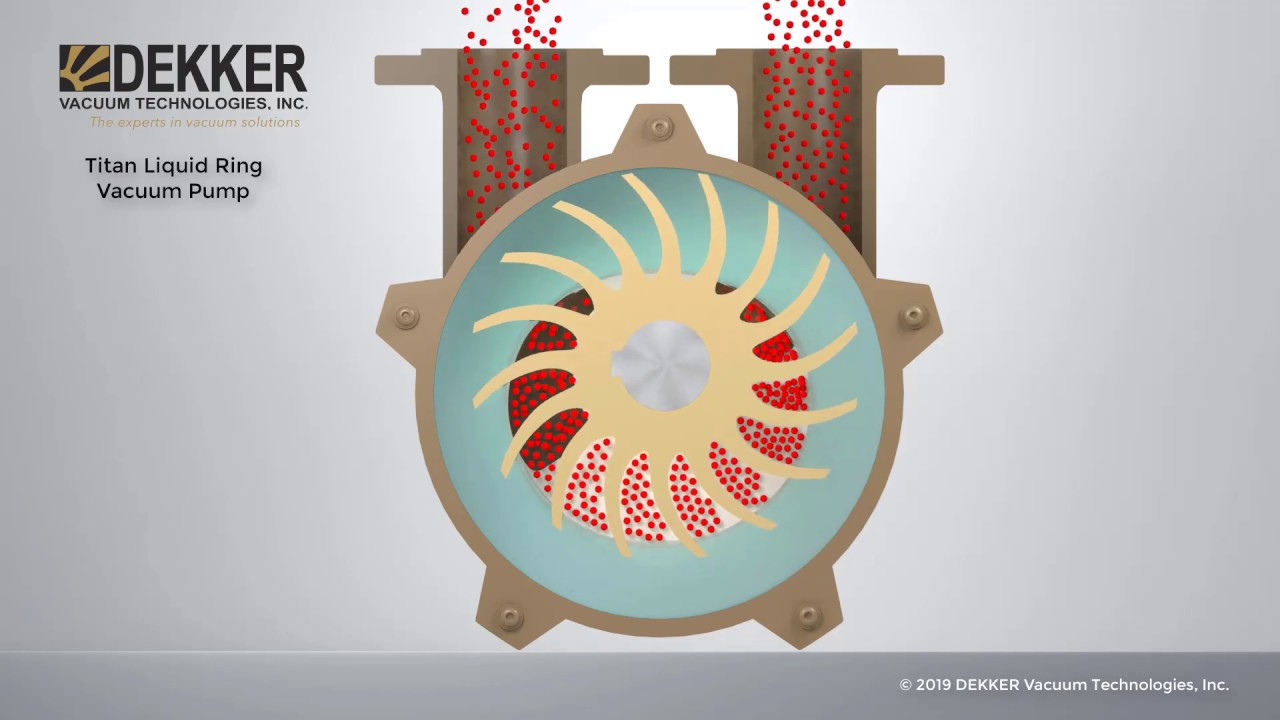
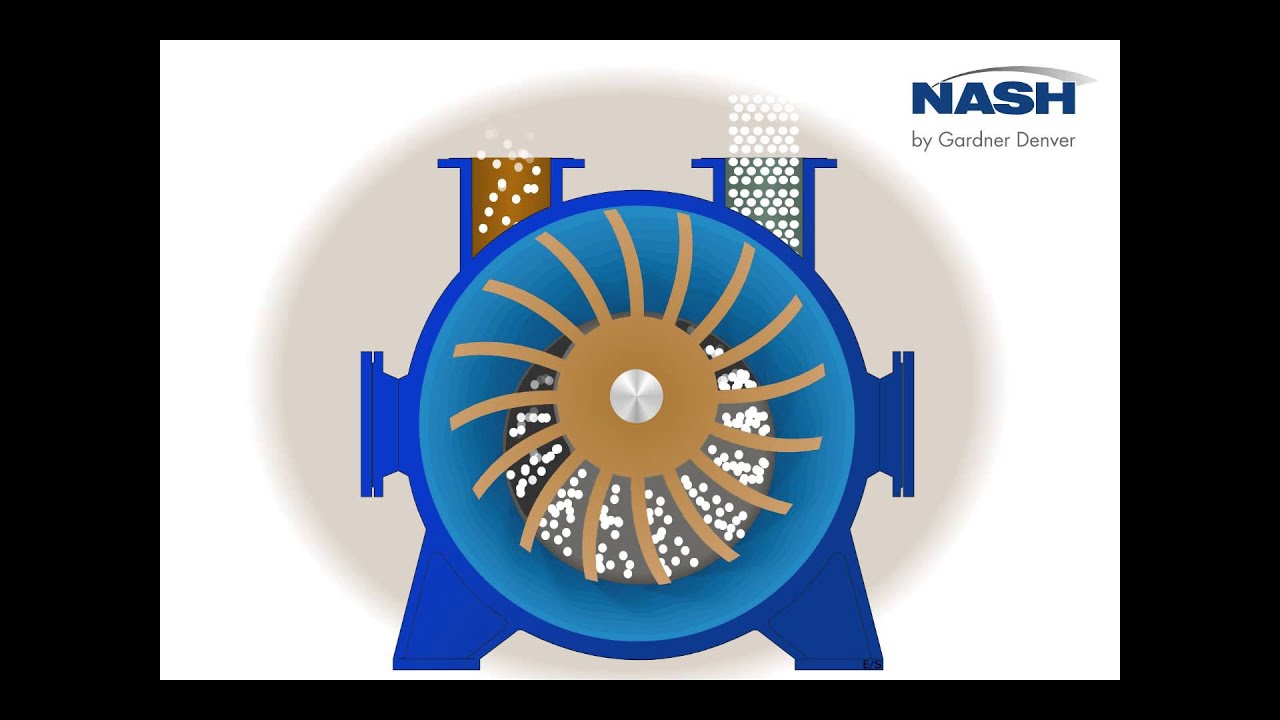
The fundamental concept behind a liquid vacuum pump's operation involves creating a low-pressure zone within the pump chamber. This is typically achieved by the rapid rotation of an impeller within a liquid-filled casing. The impeller's movement generates centrifugal force, pushing the liquid outwards and creating a low-pressure area near the center. Gases are then drawn into this low-pressure region and are subsequently compressed and discharged along with the liquid.
While the basic principle remains consistent across various types of liquid vacuum pumps, subtle differences exist in their design and operation. For instance, some pumps employ multi-stage impellers for higher vacuum levels, while others incorporate specialized mechanisms for handling corrosive gases or liquids. This diversity allows for tailored solutions across a wide range of industrial needs.
The history of liquid vacuum pump technology dates back to the early 20th century, with significant advancements driven by the demands of emerging industries. Initially, these pumps were primarily used in chemical processing and refining, but their applications quickly expanded to encompass diverse fields like pharmaceuticals, food processing, and even scientific research. Today, the continued development of liquid vacuum pump technology is fueled by the pursuit of higher efficiency, lower operating costs, and improved environmental performance.
One of the key benefits of liquid ring vacuum pumps is their tolerance to wet intake streams. Unlike dry pumps, which can be damaged by liquid ingestion, liquid ring pumps are designed to handle gas streams containing moisture or even liquid droplets. This makes them ideally suited for applications like distillation, evaporation, and drying.
Another advantage is their relatively simple design and robust construction. This translates to lower maintenance requirements and longer operating lifespans compared to some other vacuum pump technologies. Furthermore, liquid ring vacuum pumps can handle a wider range of gas compositions, including those containing condensable vapors or particulates, without significant performance degradation.
A third benefit is their ability to achieve relatively high vacuum levels, especially in multi-stage configurations. This makes them suitable for demanding applications requiring pressures significantly below atmospheric levels.
Several types of liquid vacuum pumps exist, including water ring pumps, oil ring pumps, and steam jet ejectors. Each type uses a different working fluid and offers distinct performance characteristics.
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Handles wet intake streams | Lower ultimate vacuum compared to some dry pumps |
| Simple and robust design | Higher energy consumption in some cases |
| Handles a wide range of gas compositions | Requires a continuous supply of working fluid |
Best Practices:
1. Proper fluid selection: Choose the appropriate working fluid based on the application and gas composition.
2. Regular maintenance: Implement a preventive maintenance schedule to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
3. Fluid level control: Maintain the correct fluid level in the pump to prevent damage and ensure efficient operation.
4. Inlet gas conditioning: Consider pre-treating the inlet gas stream to remove excessive moisture or particulates.
5. Discharge management: Properly manage the discharge stream, including separating and treating the liquid and gas phases.
FAQ:
1. What is the working principle of a liquid vacuum pump? A: It uses a rotating impeller within a liquid-filled casing to create a low-pressure zone.
2. What are the different types of liquid vacuum pumps? A: Common types include water ring, oil ring, and steam jet ejectors.
3. What are the applications of liquid vacuum pumps? A: They are used in various industries, including chemical processing, power generation, and pharmaceuticals.
4. What are the benefits of using a liquid vacuum pump? A: Benefits include handling wet intake streams, robust design, and handling diverse gas compositions.
5. How do I maintain a liquid vacuum pump? A: Regular maintenance includes checking fluid levels, cleaning filters, and inspecting seals.
6. What are the challenges associated with liquid vacuum pumps? A: Challenges can include cavitation, corrosion, and fluid contamination.
7. How do I choose the right liquid vacuum pump? A: Consider factors like required vacuum level, gas composition, and flow rate.
8. What is the future of liquid vacuum pump technology? A: Research and development focus on improving efficiency, reducing environmental impact, and enhancing performance.
Tips and Tricks: Regularly monitor pump performance parameters like vacuum level, flow rate, and power consumption to identify potential issues early on. Implement a robust fluid management system to ensure proper fluid quality and minimize waste.
In conclusion, understanding the liquid vacuum pump working principle is crucial for selecting and operating these essential devices effectively. Their ability to handle wet intake streams, robust design, and versatile applications make them invaluable across numerous industries. From chemical processing to power generation, liquid vacuum pumps play a vital role in achieving efficient and reliable operations. By adhering to best practices and staying informed about the latest advancements, industries can leverage the full potential of liquid vacuum pump technology. Continuous improvements in efficiency, reliability, and environmental performance position liquid vacuum pumps as a key technology for the future of vacuum applications. Further exploration of liquid vacuum pump principles can empower industries to optimize processes, reduce costs, and contribute to a more sustainable future. Embrace the power of liquid vacuum pumps and unlock new possibilities in your operations.
Find your nearest hr block office
Unlocking the outdoors your guide to the coleman sundome 6
Unlocking financial clarity mastering excel accounting spreadsheets