Unlocking DC Power: Understanding the Half Wave Rectifier Circuit
Ever wondered how your electronic devices seamlessly convert alternating current (AC) from your wall outlet into the direct current (DC) they need to function? The answer often lies in a fundamental circuit known as the half wave rectifier. This seemingly simple circuit plays a crucial role in various electronic systems, providing the foundation for DC power supply.
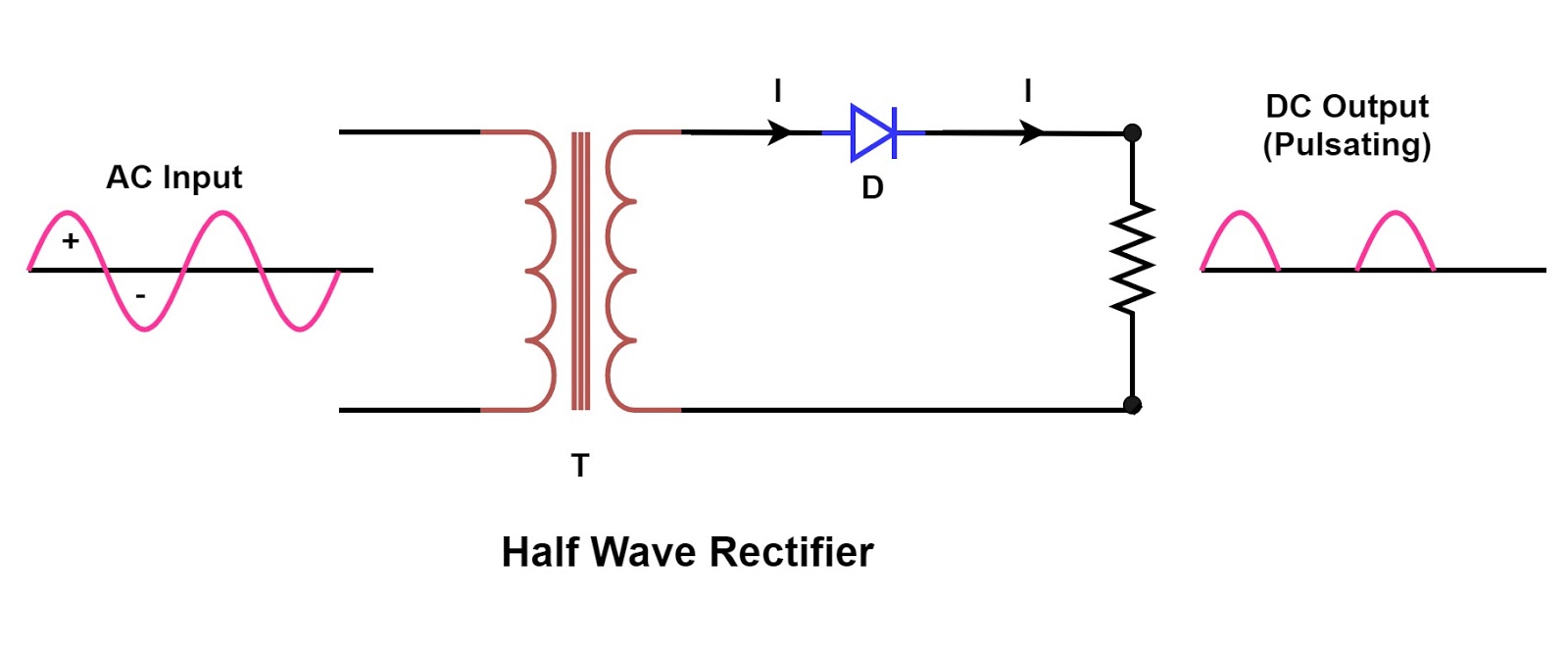
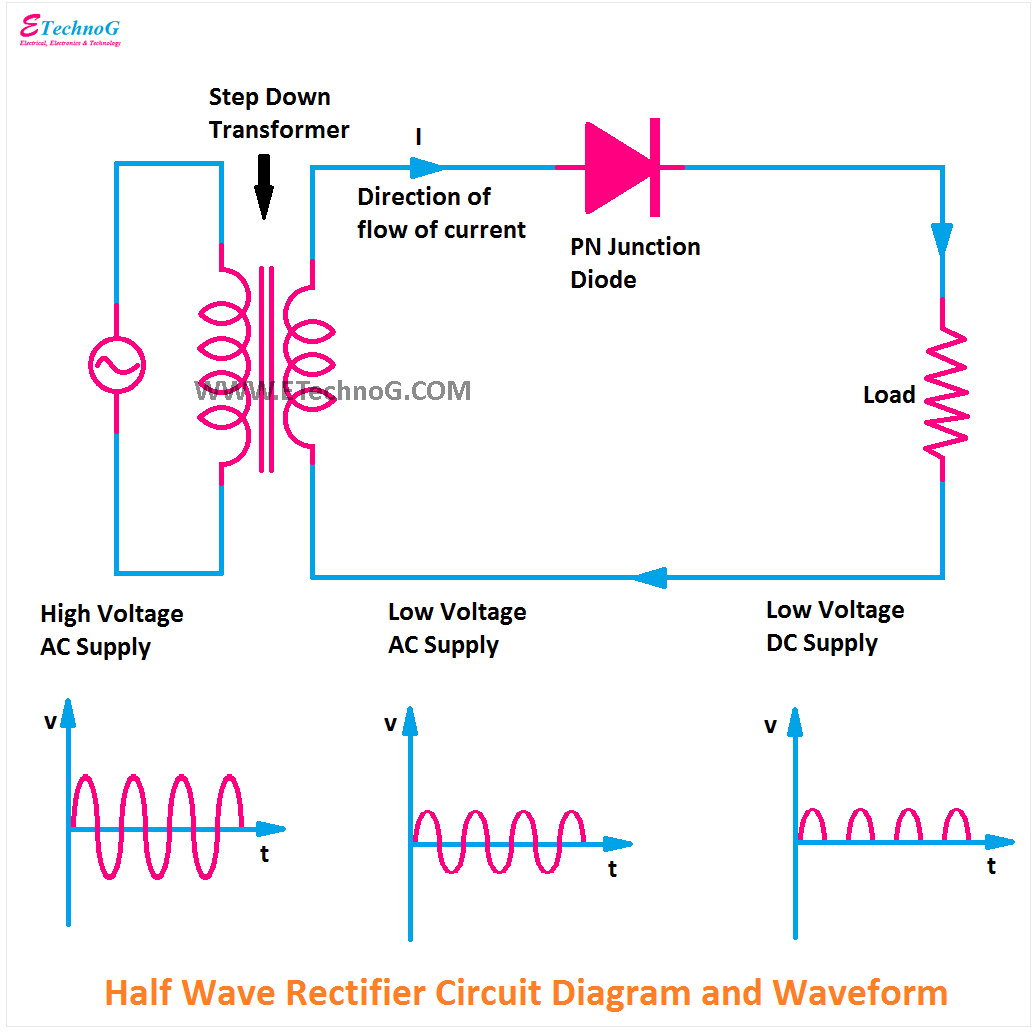
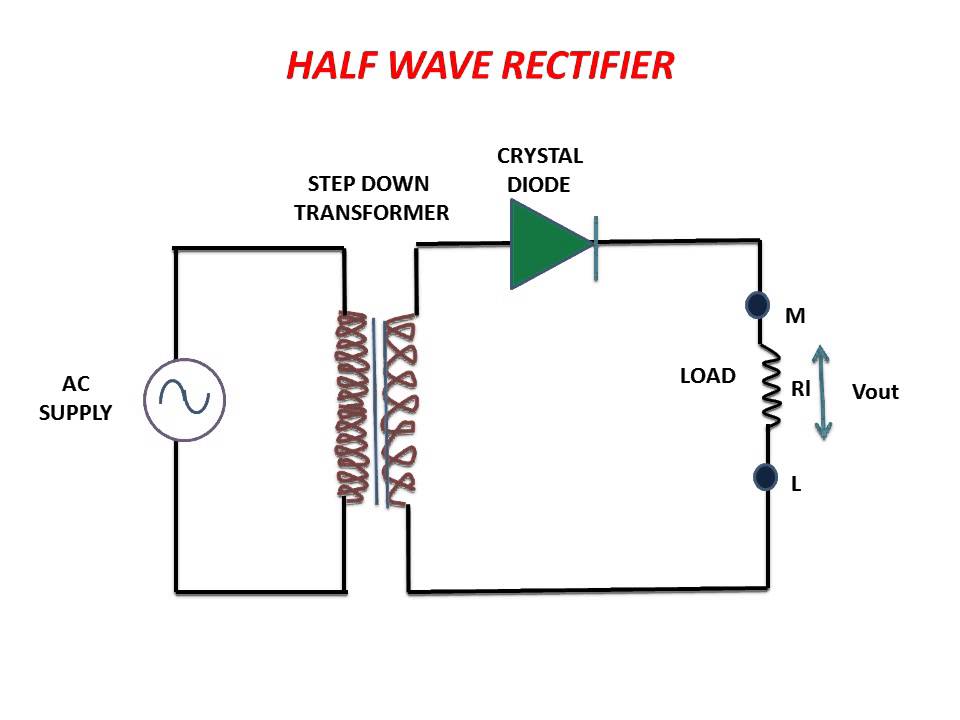
The half wave rectifier circuit diagram represents a fundamental building block in power electronics. It's the gateway to understanding how AC signals are transformed into the DC power vital for countless electronic devices. By allowing current to flow in only one direction, the half wave rectifier effectively "chops" the AC waveform, resulting in a pulsating DC output.
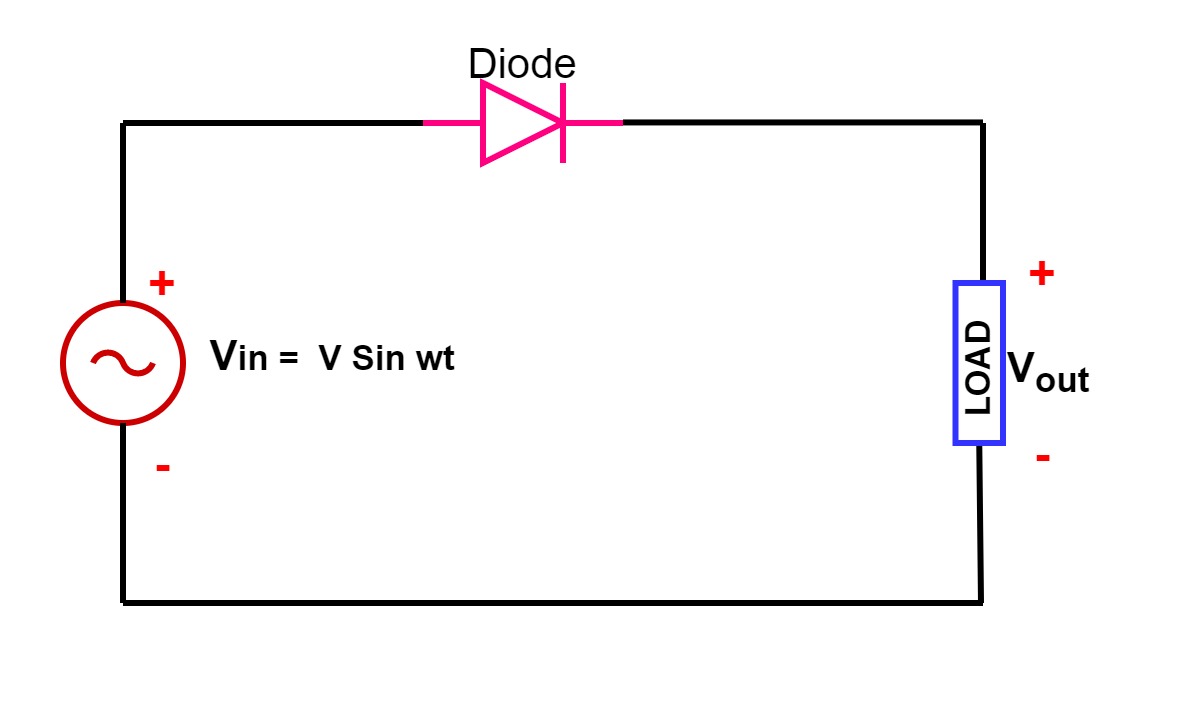
To grasp the functionality of a half wave rectifier schematic, it's essential to understand the core components. At its heart lies a single diode, a semiconductor device that acts like a one-way valve for electric current. This diode is connected in series with an AC voltage source and a load resistor. During the positive half-cycle of the AC input, the diode conducts, allowing current to flow through the load. Conversely, during the negative half-cycle, the diode blocks current flow, resulting in zero output voltage.
The historical development of rectifier circuits is closely tied to the advancements in vacuum tube technology. Early rectifiers employed vacuum tubes as diodes, enabling the conversion of AC to DC for various applications, including radio receivers. With the advent of semiconductor technology, solid-state diodes replaced vacuum tubes, leading to more compact, efficient, and reliable rectifier circuits. The half wave rectifier, in its simplicity, remains a cornerstone of power electronics.
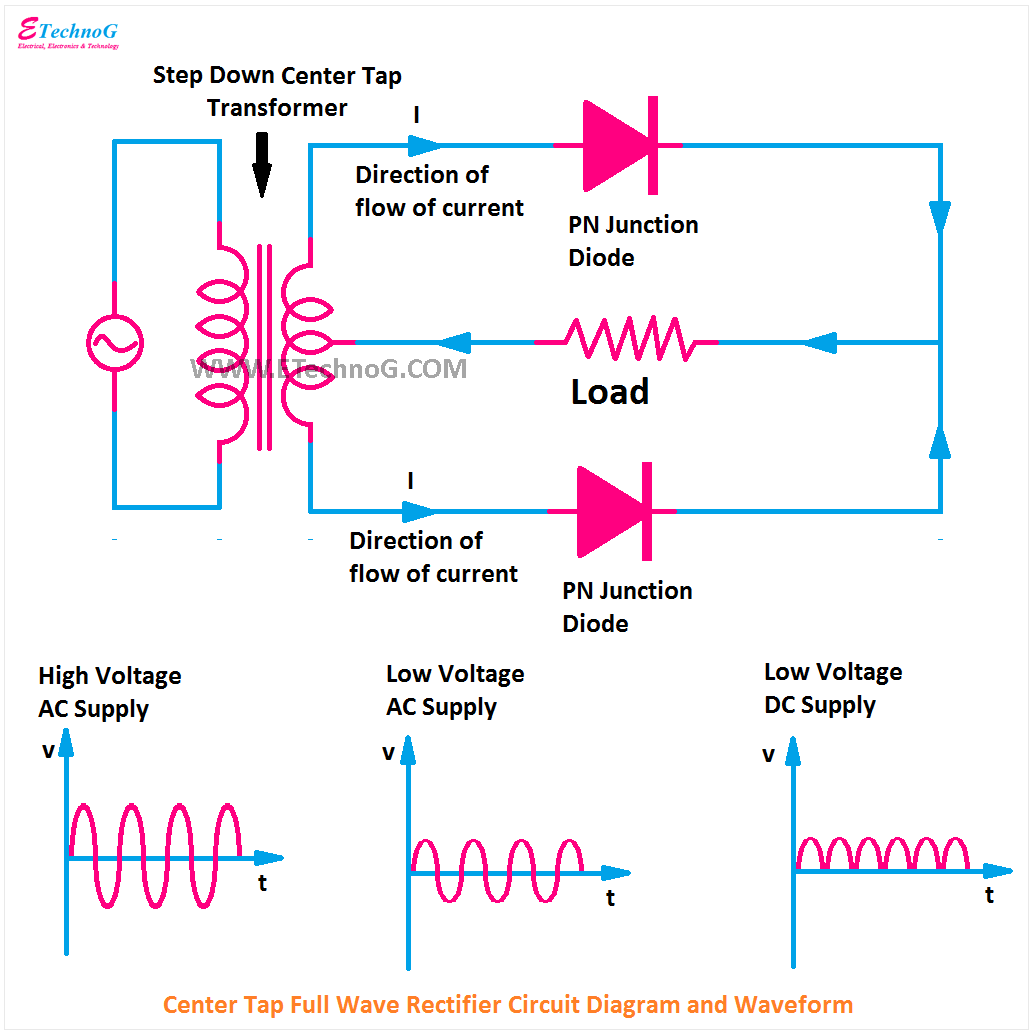
The significance of the half wave rectifier extends across a wide spectrum of applications. From simple battery chargers to complex power supplies, these circuits provide a basic means of obtaining DC power from an AC source. Understanding the half wave rectifier circuit operation is crucial for anyone working with electronics, as it forms the basis for more complex rectifier configurations like full-wave and bridge rectifiers.
A half-wave rectifier circuit diagram usually includes an AC source, a diode, and a load resistor. The diode allows current flow in one direction, effectively blocking the negative half of the AC cycle. This results in a pulsating DC output across the load resistor.
A simple example is a battery charger using a half-wave rectifier. The AC input from the mains supply is rectified to provide a pulsating DC output, which then charges the battery.
Benefits include simplicity, low cost, and ease of implementation. Its simplicity makes it a good introduction to rectifier concepts. The low component count translates to lower cost. It’s easy to implement even with basic electronic components.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Half Wave Rectifier
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Simple circuit design | Low efficiency due to utilizing only half of the AC cycle |
| Low cost due to fewer components | High ripple factor in the output DC voltage |
| Easy to implement | DC output contains significant AC components |
Best practices include selecting the appropriate diode based on the voltage and current requirements, using a suitable filter capacitor to reduce ripple, and ensuring proper heat dissipation for the diode.
Real-world examples include simple battery chargers, AC to DC adapters for low-power devices, and signal demodulation circuits in AM radios.
Frequently asked questions include: What is the purpose of a diode in a half-wave rectifier? How does the output voltage relate to the input voltage? What is the ripple factor, and how can it be reduced? What are the limitations of a half-wave rectifier?
Tips and tricks: Always check the diode polarity during circuit construction. Consider adding a filter capacitor to smooth the output voltage. Understand the limitations of a half-wave rectifier before using it in an application.
In conclusion, the half wave rectifier circuit diagram serves as a fundamental building block in electronics. Its simplicity, low cost, and ease of implementation make it an essential component in numerous applications, from basic AC to DC conversion to complex power supplies. While the half-wave rectifier has its limitations, such as low efficiency and high ripple, understanding its operation is crucial for anyone working with electronics. Mastering the half wave rectifier circuit diagram provides a solid foundation for exploring more complex rectifier configurations and ultimately contributes to a deeper appreciation of how electronic devices harness the power they need. By exploring its functionality, advantages, and disadvantages, we can effectively utilize this essential circuit in a variety of applications. Continue learning and experimenting with half-wave rectifiers to expand your knowledge of electronics and unlock new possibilities.
Walmart grocery pickup with ebt a complete guide
Tampa bay power outages your guide to tecos outage map
Power up your ring 2 doorbell transformer installation guide

.jpg)