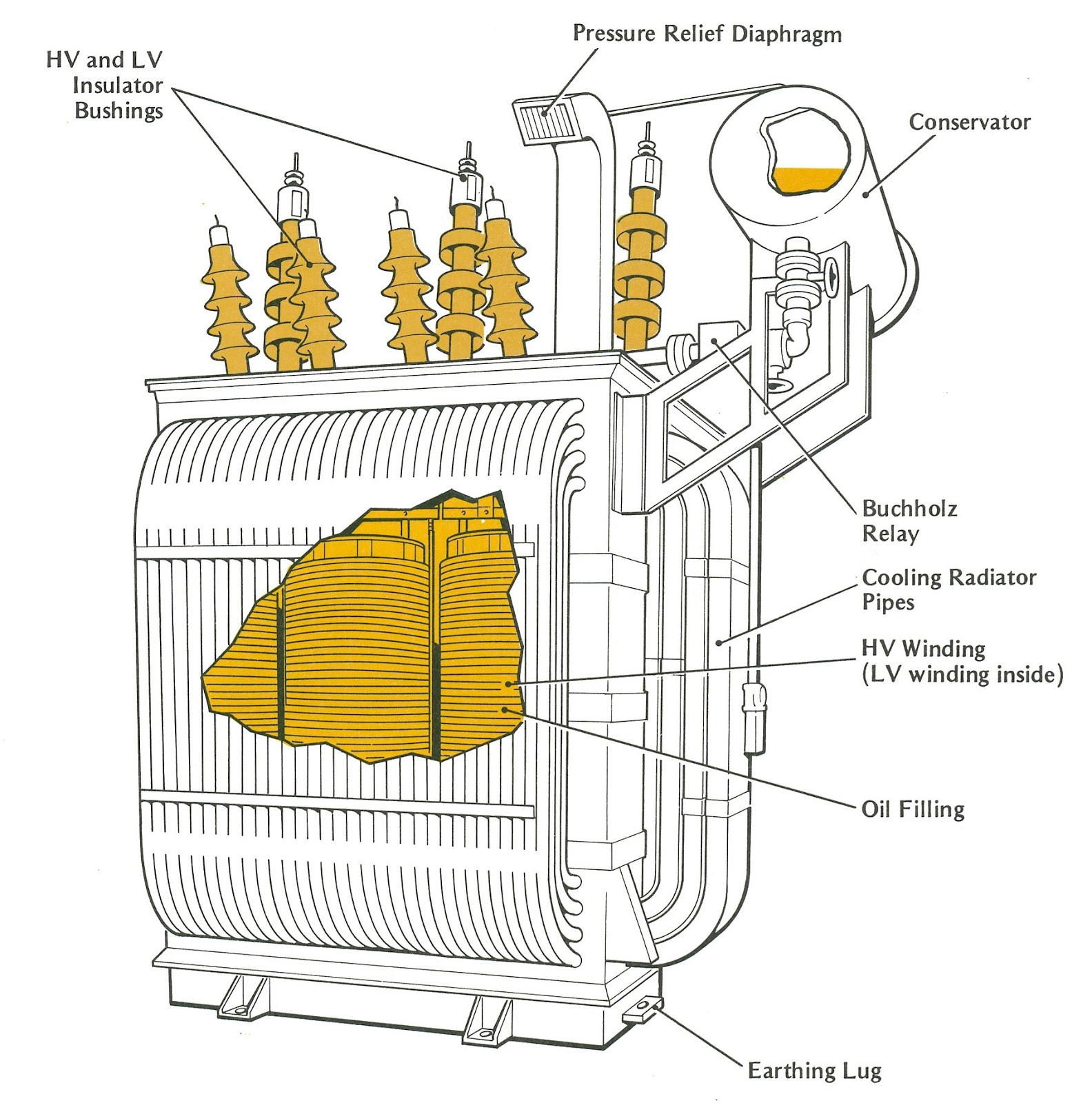
Understanding Power Line Transformers
Ever wondered how electricity makes its way from power plants to your home? A critical component in this journey is the power line transformer, a device that silently hums away, ensuring you have the electricity you need. These unassuming metal boxes are essential for efficient and safe power distribution.
Power line transformers, also known as distribution transformers, modify voltage levels on the electrical grid. They step down the high voltage transmitted over long distances to the lower voltage suitable for residential and commercial use. This voltage conversion is crucial for preventing damage to appliances and ensuring user safety.
The story of power line transformers begins with the principles of electromagnetic induction discovered by Michael Faraday and Joseph Henry in the 19th century. Early transformers were crude and inefficient, but the need for efficient power distribution spurred rapid innovation. The development of laminated cores and improved insulation materials significantly enhanced transformer performance and paved the way for the modern electrical grid.
The importance of these transformers in our modern world is undeniable. They are the backbone of the power distribution system, allowing electricity to be transmitted efficiently over long distances and then safely delivered to consumers. Without them, our reliance on electricity for everything from lighting and heating to powering our digital devices would be impossible.
However, power line transformers face several challenges. Environmental factors like extreme temperatures and lightning strikes can affect their performance and lifespan. Regular maintenance and monitoring are essential to ensure reliable operation and prevent costly failures. Maintaining these critical components involves inspections, oil analysis, and sometimes even replacement.
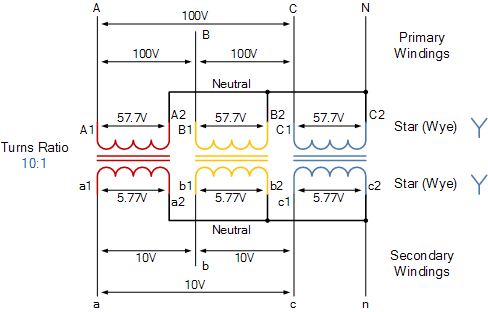
A power line transformer works by utilizing the principle of electromagnetic induction. An alternating current flowing through the primary winding creates a changing magnetic field, which induces a voltage in the secondary winding. The ratio of the number of turns in the primary and secondary windings determines the voltage transformation ratio. For example, a transformer with 1000 turns in the primary winding and 100 turns in the secondary winding will step down the voltage by a factor of 10.
One of the key benefits of power line transformers is increased efficiency in power transmission. By stepping up voltage for long-distance transmission, line losses due to resistance are minimized. This reduces energy waste and saves costs. Additionally, using lower voltages at the consumer end enhances safety and protects electrical equipment.
Another advantage is the ability to customize voltage levels. Different appliances and equipment require different voltages. Power line transformers allow the electricity provider to deliver the appropriate voltage level for various applications, from residential homes to industrial facilities.
Implementing power line transformers effectively involves careful planning and consideration of various factors. Proper sizing is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and preventing overload. Regular maintenance, including oil analysis and visual inspections, helps detect potential problems early on. Protecting transformers from environmental factors like lightning and extreme temperatures is also important.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Power Line Transformers
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Increased efficiency in power transmission | Potential for humming noise |
| Enhanced safety for consumers | Susceptibility to environmental factors |
| Customization of voltage levels | Requires regular maintenance |
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is the function of a power line transformer? A power line transformer changes voltage levels on the electrical grid.
2. Why are transformers important? They allow efficient power transmission and safe voltage levels for consumers.
3. How do transformers work? They use electromagnetic induction to change voltage.
4. What are some challenges faced by power line transformers? Environmental factors and the need for regular maintenance.
5. How can transformer lifespan be extended? Regular maintenance and protection from the elements.
6. What are the different types of power line transformers? Common types include single-phase and three-phase transformers.
7. What safety precautions should be taken around power line transformers? Never touch a transformer and stay away from downed power lines.
8. How can I learn more about power line transformers? Resources like IEEE and electrical engineering textbooks provide in-depth information.
In conclusion, power line transformers are indispensable components of the modern electrical grid. They facilitate efficient power transmission, ensure consumer safety, and enable the reliable delivery of electricity to homes and businesses. Understanding their function, benefits, and challenges is crucial for appreciating the complex infrastructure that powers our world. By implementing best practices for maintenance and operation, we can maximize their lifespan and ensure the continued flow of electricity that fuels our daily lives. Regular inspections, proper grounding, and proactive mitigation of environmental risks are key to reliable power distribution. Investing in the health and longevity of power line transformers is an investment in the future of our electrical infrastructure. As technology advances, continued research and development in transformer technology will further enhance the efficiency and reliability of our power grid.
Finding the perfect rav4 hybrid limited near you
Level up your roblox persona the ultimate guide to aesthetic usernames for boys
Master the art of stone skipping