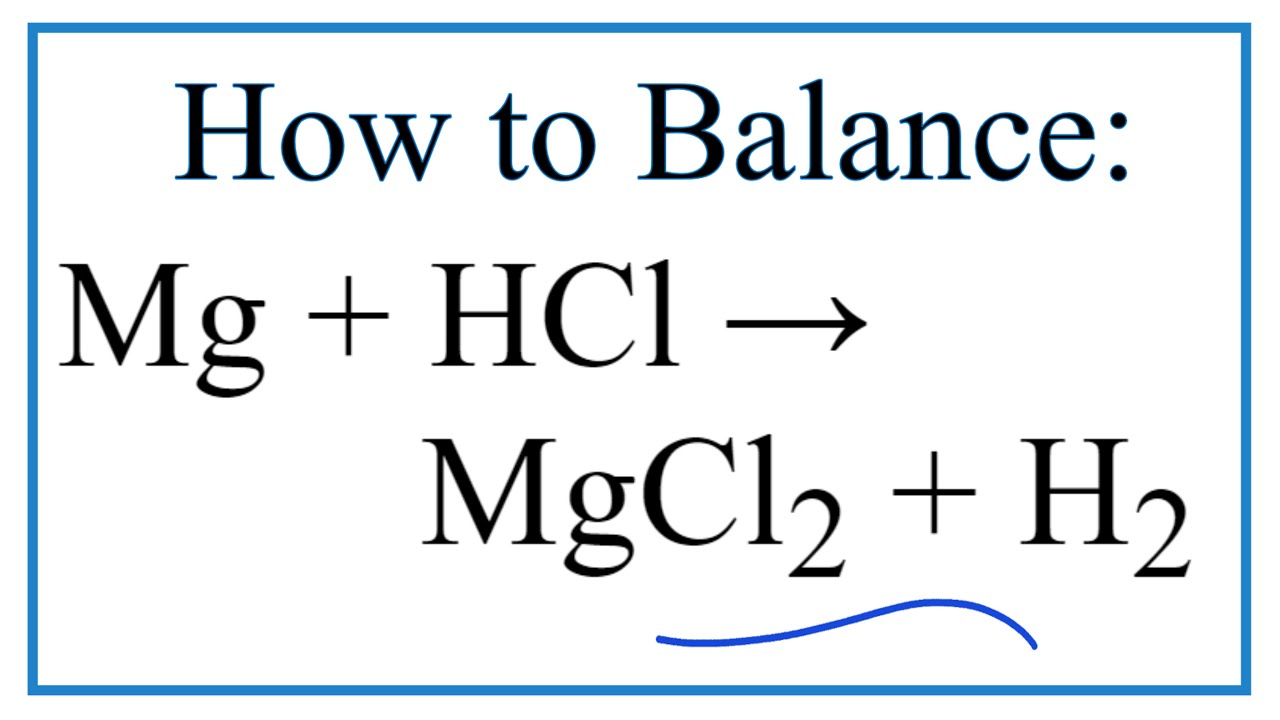
The Intriguing Story of Hydrochloric Acid Production

From the depths of our stomachs to the heart of industrial processes, hydrochloric acid, often abbreviated as HCl, plays a vital, often unseen, role in our world. But how is this potent substance, capable of both dissolving metals and aiding digestion, brought into being? The creation of hydrochloric acid is a tale of chemical ingenuity, weaving together elements in a delicate dance of reactions. Let's delve into the fascinating world of HCl production.
The synthesis of hydrochloric acid is a process with a rich history, dating back centuries. Early alchemists stumbled upon its creation, observing the pungent fumes released when common salt was mixed with vitriol (sulfuric acid). These initial, rudimentary methods paved the way for the sophisticated industrial processes we employ today. Understanding the historical context of HCl production reveals not just the scientific advancements, but also the evolving relationship between humans and the chemical world.
The hydrochloric acid manufacturing process primarily revolves around the reaction between hydrogen gas and chlorine gas. This seemingly simple reaction, however, demands precise control and careful handling due to the volatile nature of the reactants. Hydrogen chloride gas, the product of this reaction, is then dissolved in water to produce the final hydrochloric acid solution. The concentration of the acid can be adjusted by varying the amount of hydrogen chloride gas dissolved.
The significance of hydrochloric acid production extends far beyond the laboratory. This versatile chemical plays a critical role in various industries, from steel production and oil refining to food processing and pharmaceutical manufacturing. The ability of HCl to dissolve metal oxides makes it invaluable in cleaning metal surfaces before galvanizing or other treatments. In the food industry, it’s used to regulate pH and produce hydrolyzed vegetable protein. The widespread applications of HCl underscore the importance of its efficient and safe production.
Modern methods for generating hydrochloric acid involve careful control of temperature, pressure, and the purity of the reactants to ensure a high-quality product. The process often involves multiple steps, including purification of the hydrogen chloride gas before dissolving it in water. This attention to detail is essential for minimizing impurities and maximizing the effectiveness of the resulting acid.
The synthesis of hydrochloric acid is most commonly achieved through the direct reaction of hydrogen and chlorine gases, a process that produces hydrogen chloride gas. This gaseous HCl is then absorbed into water, creating the hydrochloric acid solution.
Benefits of controlled HCl production include: consistent product quality, enhanced safety measures, and minimized environmental impact. Standardized processes ensure a reliable supply of acid with the required specifications. Safety protocols throughout the production chain mitigate the risks associated with handling hazardous chemicals. Modern methods also focus on minimizing waste and emissions, promoting environmentally responsible production.
An action plan for safe HCl production involves rigorous safety protocols, including proper ventilation, protective gear, and emergency response procedures. Successful implementation requires ongoing training and monitoring to maintain a safe working environment.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Industrial HCl Production
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Large-scale production capabilities | Potential for hazardous chemical releases |
| Cost-effective production methods | Requires specialized equipment and infrastructure |
| High purity product achievable | Energy intensive process |
Best practices for HCl production involve using high-purity reactants, precise control of reaction parameters, and efficient absorption systems. Continuous monitoring and quality control checks are crucial for maintaining product consistency and safety.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is the primary method for producing hydrochloric acid? (Combining hydrogen and chlorine gas, followed by dissolving the resulting hydrogen chloride in water.)
2. What are some common uses of HCl? (Steel pickling, pH regulation, food processing, chemical synthesis.)
3. Why is safety crucial in HCl production? (Due to the corrosive and hazardous nature of the chemicals involved.)
4. How is the concentration of HCl controlled? (By regulating the amount of hydrogen chloride gas dissolved in water.)
5. What are the environmental concerns related to HCl production? (Potential release of chlorine gas and the need for responsible waste management.)
6. What are the historical origins of HCl production? (Discovered by alchemists through reactions involving salt and sulfuric acid.)
7. What are some alternatives to industrial HCl production? (Electrolysis of brine solutions.)
8. What are the key factors affecting the efficiency of HCl production? (Purity of reactants, temperature, pressure, and the absorption process.)
Tips and tricks for optimizing HCl production often involve improving the efficiency of the absorption process and minimizing waste generation through process optimization.
The production of hydrochloric acid is a remarkable feat of chemical engineering, a testament to our ability to harness the power of chemical reactions for both industrial and everyday applications. From its intriguing historical roots to its essential role in modern society, HCl production underscores the interconnectedness of science, technology, and human progress. Understanding the intricacies of how hydrochloric acid is made allows us to appreciate the complex processes that bring forth essential materials and empowers us to continue innovating for a safer and more efficient future. Continuous improvement in production methods, coupled with stringent safety protocols, will further enhance the sustainability and effectiveness of this vital chemical process. By embracing responsible practices and ongoing research, we can ensure that the benefits of HCl production are maximized while minimizing its potential risks, paving the way for a future where science and industry work in harmony with the environment.
Revitalizing your drive the toyota rav4 hybrid battery replacement guide
Fun and creative nail art for kids
Pimp your ride the wild world of vinyl car wraps