Navigating BUN Levels Naturally

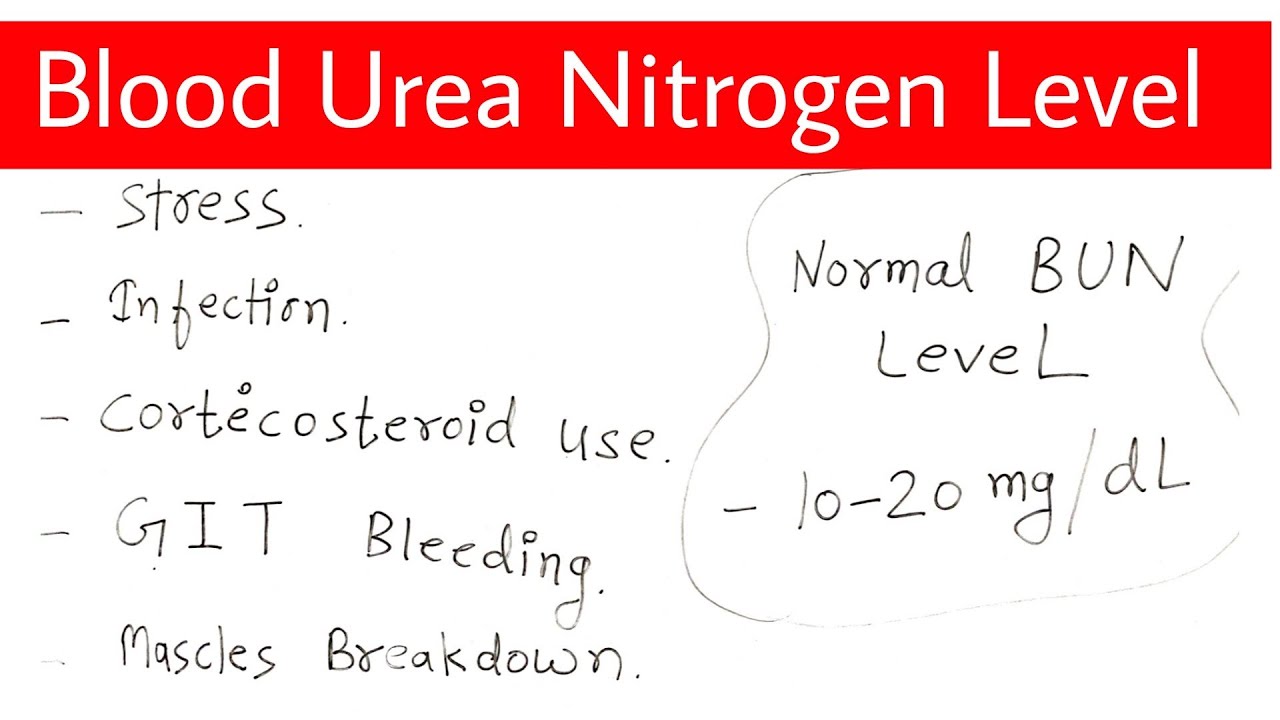
Ever wonder what those little letters "BUN" on your blood test results mean? BUN stands for blood urea nitrogen, a measure of waste product in your blood. Elevated BUN levels can signal kidney issues, and while medical intervention is sometimes necessary, there are many things you can do to support healthy BUN levels naturally. This journey towards better kidney health starts with understanding what BUN is and how lifestyle choices impact it.
BUN is a byproduct of protein metabolism. When your body breaks down protein, it creates urea, which is then filtered out by your kidneys and removed through urine. High BUN levels, often referred to as azotemia, can suggest that your kidneys aren't functioning optimally. This could be due to a variety of factors, ranging from dehydration to more serious kidney conditions. Understanding your individual situation is crucial, which is why consulting with a healthcare professional is always the first step.
The importance of maintaining healthy BUN levels cannot be overstated. Your kidneys are essential for filtering waste and maintaining the body's fluid balance. When BUN levels are elevated, it puts extra strain on these vital organs. Addressing high BUN can help prevent further kidney damage and contribute to overall well-being.
Historically, understanding and managing BUN has been a significant development in healthcare. It has allowed doctors to gain insights into kidney function and develop strategies to address related health issues. From simple lifestyle adjustments to more advanced medical interventions, the ability to measure and interpret BUN has been instrumental in improving kidney health.
Managing BUN levels involves a multifaceted approach. One of the primary ways to lower BUN is by increasing hydration. Drinking plenty of water helps flush out excess urea, easing the burden on your kidneys. Dietary changes, such as reducing protein intake, can also make a difference. Focusing on high-quality protein sources and limiting processed foods can significantly contribute to healthier BUN levels.
Lowering BUN can offer several benefits. First, it promotes healthier kidney function, reducing the risk of further complications. Second, it can improve overall energy levels, as the body isn't working as hard to filter waste. Third, it can contribute to better blood pressure regulation, as kidney health is intrinsically linked to cardiovascular health.
An action plan for lowering BUN might include: 1) Consulting with a doctor to understand the underlying cause of elevated BUN. 2) Tracking your daily water intake and aiming for at least eight glasses a day. 3) Evaluating your protein intake and making adjustments as needed with guidance from a dietitian. 4) Incorporating regular exercise into your routine to promote overall health and kidney function.
Recommendations for managing BUN: Consult with a nephrologist or registered dietitian. They can provide personalized guidance based on your individual needs and health status. Numerous online resources also offer valuable information, including the National Kidney Foundation website.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Reducing BUN Levels
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Improved kidney function | Potential dietary restrictions |
| Increased energy levels | Need for ongoing monitoring |
Best practices include: staying hydrated, eating a balanced diet, managing underlying health conditions, regular exercise, and regular check-ups.
Real-world examples include individuals who have successfully lowered their BUN through lifestyle changes like increased hydration and dietary modifications, as guided by their healthcare providers.
Challenges in lowering BUN can include difficulty adhering to dietary restrictions, underlying health conditions, and access to resources. Solutions include working with a dietitian, managing underlying conditions with medication as prescribed, and seeking support from healthcare professionals.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is BUN? - BUN is a measure of urea nitrogen in the blood.
2. What causes high BUN? - High BUN can be caused by various factors, including dehydration and kidney disease.
3. How can I lower my BUN? - Lowering BUN can involve increased hydration and dietary modifications.
4. Is high BUN dangerous? - High BUN can indicate underlying health issues and should be addressed.
5. What foods should I avoid with high BUN? - Foods high in protein might need to be limited.
6. How much water should I drink to lower BUN? - Aim for at least eight glasses of water a day, but consult your doctor.
7. Can exercise help lower BUN? - Regular exercise can support overall health, including kidney function.
8. How often should I check my BUN levels? - Regular monitoring is important; consult your doctor for frequency.
Tips and tricks for lowering BUN: Carry a water bottle with you throughout the day. Prepare healthy meals and snacks in advance. Find an exercise routine you enjoy and can stick with.
Maintaining healthy blood urea nitrogen levels is a crucial component of overall health and well-being. By understanding the factors that influence BUN and making informed choices about diet, hydration, and lifestyle, you can take proactive steps to support your kidneys and improve your quality of life. Addressing elevated BUN often involves a combination of lifestyle changes and medical guidance, so working closely with your healthcare provider is essential. Don't hesitate to reach out to your doctor to discuss any concerns about your BUN levels and explore the best strategies for your individual needs. Remember, taking care of your kidneys is an investment in your long-term health, so start prioritizing them today.
Understanding bloods gang leadership
Unlocking the power of sherwin williams gorgeous white a comprehensive guide
Nc state employee payday