Decoding the Three-Post GM Starter Solenoid

Ever wondered about that small cylindrical component nestled near your GM vehicle's starter? It's the starter solenoid, a critical part of the starting system, and in many GM vehicles, it takes the form of a three-post design. Understanding its function can empower you to troubleshoot starting issues and keep your car running smoothly.
The three-post GM starter solenoid acts as an electrical relay and a powerful switch. Imagine trying to send a massive surge of electricity directly through your ignition key. It wouldn't work! The solenoid bridges this gap, taking a small electrical signal from the ignition and using it to engage a high-current circuit that activates the starter motor.
This seemingly simple device plays a pivotal role. Without a functioning starter solenoid, your engine wouldn't crank. The solenoid ensures a safe and efficient transfer of power, protecting your car's electrical system from overload.
Delving into the workings of this three-post configuration is essential for any GM owner. It's a system that has been around for decades, evolving alongside automotive technology. Its core function remains the same: to provide a reliable starting mechanism. Understanding its operation helps diagnose common problems, saving you time and potentially costly repairs.
This article aims to demystify the three-post GM starter solenoid, exploring its inner workings, common issues, troubleshooting techniques, and best practices. We'll break down complex concepts into digestible pieces, empowering you to tackle starter problems with confidence.
The three-post solenoid’s history is intertwined with the development of the electric starter motor itself. Early vehicles used hand cranks, a notoriously dangerous and laborious process. The electric starter, coupled with the solenoid, revolutionized vehicle operation, making it significantly easier and safer to start an engine. The three-post design became a common feature in many GM vehicles, a testament to its effectiveness and reliability.
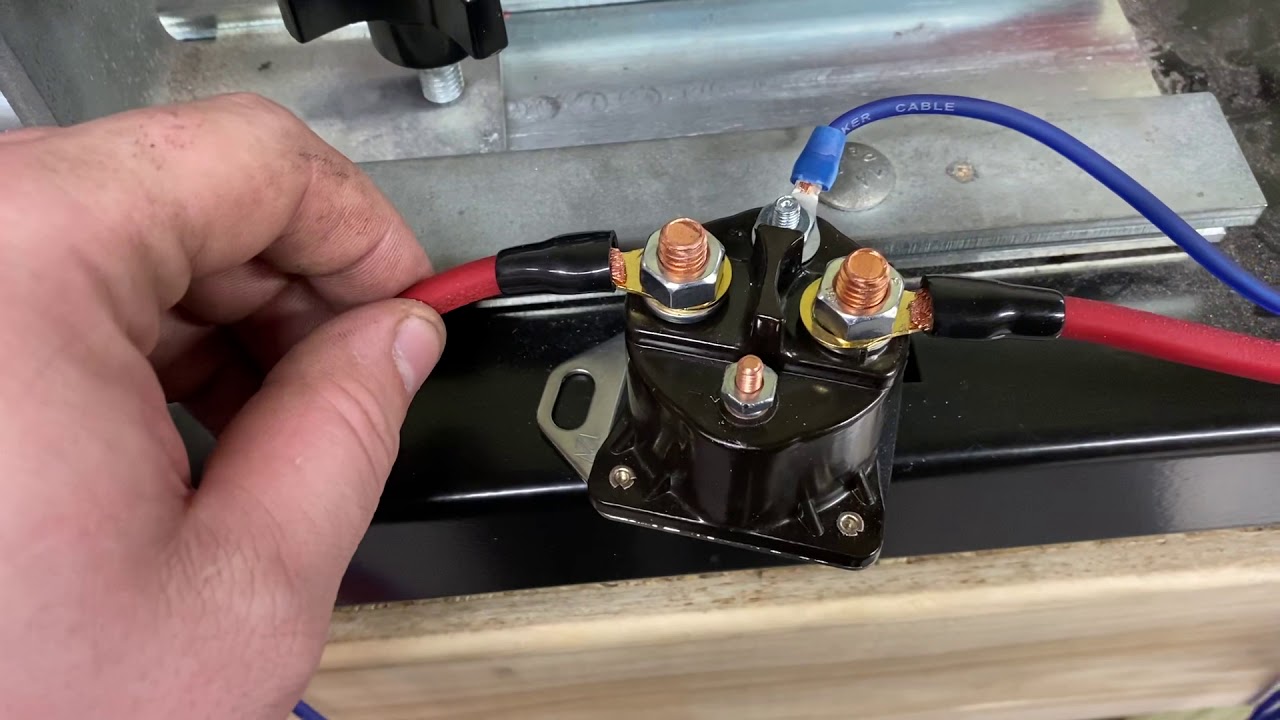
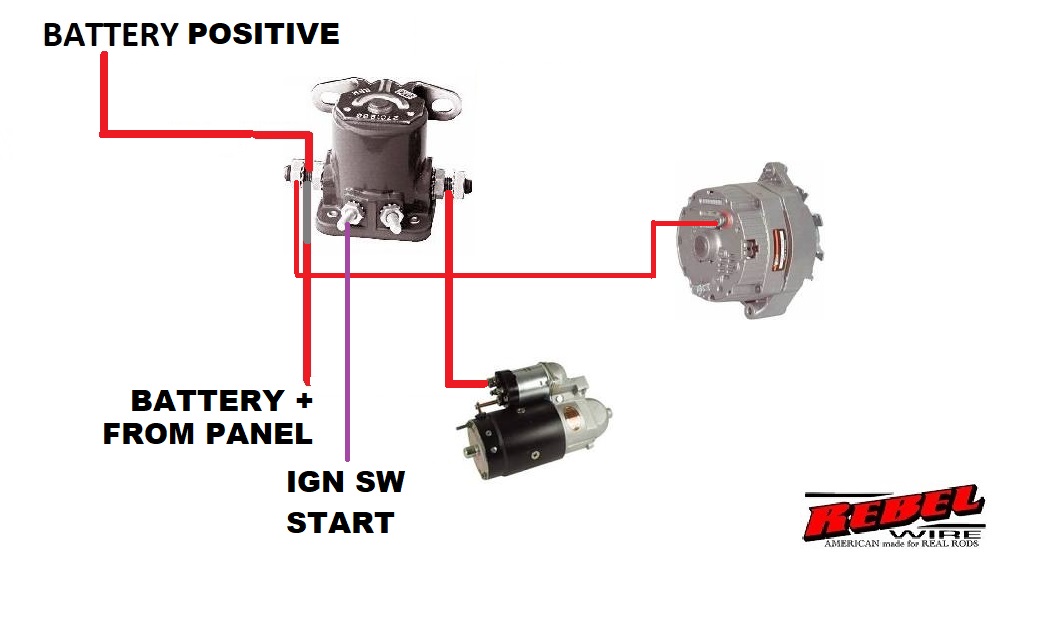
The three posts on the solenoid each have a distinct function. The "S" terminal receives the small electrical signal from the ignition switch. The "B" terminal connects to the battery's positive terminal, supplying the high current needed to crank the engine. The "M" terminal sends power to the starter motor once the solenoid is activated. This setup enables a controlled and powerful engagement of the starter motor.
One common issue is a clicking sound when turning the key, indicating a faulty solenoid. This could stem from a bad connection, a depleted battery, or a malfunctioning solenoid itself. Testing the solenoid with a multimeter can help pinpoint the problem.
Benefits of Understanding the Three-Post GM Starter Solenoid
1. Simplified Troubleshooting: Knowing how the solenoid works empowers you to diagnose starting problems accurately, eliminating guesswork and unnecessary repairs.
2. Cost Savings: By understanding the solenoid’s function, you can often identify and fix simple issues yourself, avoiding costly mechanic visits.
3. Increased Confidence: Empower yourself with the knowledge to maintain and repair a crucial component of your vehicle, boosting your confidence as a car owner.
Troubleshooting Tips:
Check battery connections for corrosion or looseness. Use a multimeter to test voltage at the solenoid terminals. If no power reaches the "S" terminal when the key is turned, the issue may lie in the ignition switch circuit. If the solenoid clicks but the starter doesn't engage, the solenoid itself may be faulty.
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Reliable Starting | Can be susceptible to corrosion |
| Simple Design | Requires proper maintenance |
| Easy to Test | Can fail over time |
FAQ:
1. What is the function of a starter solenoid? A: It acts as a relay, engaging the starter motor.
2. How many posts does a GM starter solenoid have? A: Typically three: S, B, and M.
3. What does a clicking solenoid indicate? A: Potential problems with the solenoid, battery, or wiring.
4. How can I test a starter solenoid? A: Use a multimeter to check voltage at the terminals.
5. Can I replace a starter solenoid myself? A: Yes, it is often a straightforward procedure.
6. What causes a starter solenoid to fail? A: Corrosion, excessive heat, or electrical overload.
7. How do I prevent starter solenoid problems? A: Keep connections clean and ensure a healthy battery.
8. Where is the starter solenoid located? A: Usually near the starter motor, often bolted to it.
Understanding the three-post GM starter solenoid is essential for any GM vehicle owner. This small but powerful component plays a critical role in starting your engine. By familiarizing yourself with its operation, troubleshooting techniques, and best practices, you can maintain a reliable starting system and avoid potential headaches down the road. Regular checks, cleaning connections, and prompt attention to any unusual sounds can prolong the life of your solenoid and ensure smooth starts every time. Armed with this knowledge, you'll be better equipped to handle starting issues, saving you time, money, and frustration. Remember, a well-maintained starting system is key to a trouble-free driving experience.
Haunting images unmasking the reality of wwi through soldier photography
Unlocking victory deuce statistics in tennis
Crafting the perfect tiktok display name ideas and strategies