Decoding the Ground Wire: Electrical Safety and Color Codes
Ever wonder about that often-overlooked, unassuming green (or sometimes bare) wire in your electrical system? It's not there for decoration. That's your ground wire, a critical safety component protecting you, your home, and your electronics from electrical faults. Understanding its function, and more importantly, its color coding, is paramount for any homeowner, DIY enthusiast, or anyone working with electricity.
The color of the earth wire, as it's sometimes called, provides a universally recognized visual identifier for this vital safety feature. Incorrect grounding or misidentification of the ground conductor can have serious consequences, from electrical shocks to fires. This seemingly minor detail plays an oversized role in electrical safety.
Identifying the ground wire by its color is the first step in ensuring a properly grounded electrical system. This simple visual cue allows electricians and homeowners alike to quickly and accurately connect the ground wire, minimizing the risk of dangerous wiring errors. The standardization of ground wire colors provides a common language for electrical safety across different regions and installations.
Historically, grounding practices weren't always standardized. Early electrical systems lacked dedicated grounding, leading to a higher risk of electrical hazards. The adoption of color-coded ground wires marked a significant step forward in electrical safety, providing a clear and consistent way to identify this important conductor.
The importance of the ground wire color can't be overstated. It facilitates safe electrical installations, reduces the risk of electrical shocks and fires, and ensures the proper functioning of sensitive electronic equipment. Imagine trying to troubleshoot a complex wiring issue without a clear visual identifier for the ground wire – the process would be significantly more challenging and potentially dangerous.
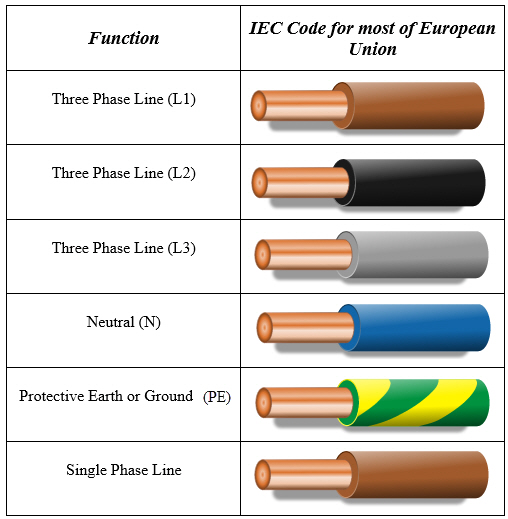
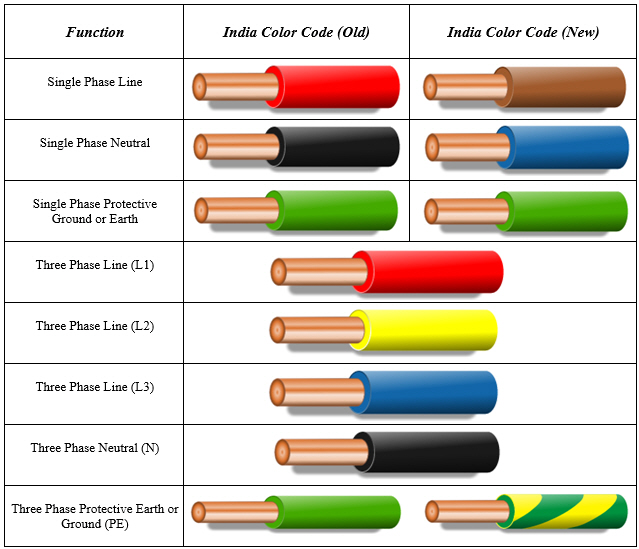
In most modern wiring systems, the ground wire is identified by its green insulation. Sometimes, you might encounter a bare, uninsulated copper wire serving as the ground. These color codes provide instant recognition, allowing for efficient and safe wiring practices.
One of the primary benefits of a color-coded ground wire is enhanced safety. In the event of a fault, the ground wire provides a low-resistance path for excess current to flow safely to the earth, protecting you from shock and preventing damage to your appliances.
Proper grounding also protects sensitive electronic equipment. The ground wire helps to stabilize voltage levels and reduce electrical noise, ensuring the reliable operation of computers, televisions, and other sensitive devices.
A third benefit is simplified troubleshooting. The easily identifiable ground wire simplifies the process of diagnosing and repairing electrical problems, saving time and reducing frustration.
When working with electrical wiring, always double-check the ground wire connection. Ensure it's securely fastened to the designated grounding point in your electrical panel and to the grounding screw on outlets and appliances.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Color-Coded Ground Wires
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Safety | Color Blindness Can Pose Challenges |
| Simplified Troubleshooting | Older Systems May Not Adhere to Current Standards |
| Protection of Electronic Equipment | Damage to Insulation Can Obscure Color |
Best Practices:
1. Always verify the ground wire color before making any connections.
2. Use appropriate connectors and ensure tight connections.
3. Never use the ground wire for any purpose other than grounding.
4. Periodically inspect your wiring to ensure the ground wire is intact and properly connected.
5. Consult with a qualified electrician if you're unsure about any aspect of your electrical system.
FAQ:
1. What color is the ground wire in most electrical systems? Green or bare copper.
2. Why is the ground wire important? It protects against electrical shocks and equipment damage.
3. Can I use a different colored wire for grounding? No, always use the designated green or bare copper wire.
4. What should I do if my ground wire is damaged? Contact a qualified electrician immediately.
5. How do I test my ground connection? Use a receptacle tester available at most hardware stores.
6. Is it safe to work on electrical wiring myself? If you're not experienced, it's best to consult a qualified electrician.
7. What are the signs of a faulty ground connection? Frequent tripping of circuit breakers, tingling sensation when touching appliances, or flickering lights.
8. How often should I check my grounding system? At least once a year.
Tips & Tricks: When working with electrical wiring, always turn off the power at the breaker box before making any connections.
Understanding the color of your ground wire is a fundamental aspect of electrical safety. It's a simple yet vital piece of knowledge that can prevent serious accidents and protect your valuable electronics. From basic identification to advanced troubleshooting, recognizing the green or bare copper conductor is the cornerstone of a safe and reliable electrical system. By following best practices and staying informed about ground wire color codes, you can ensure the safety of your home and family. Don't underestimate the importance of this small but crucial safety feature – take the time to learn about it, and always prioritize safety when working with electricity. Remember, when in doubt, consult a qualified electrician for expert advice and assistance. Your safety is worth it. Investing in your understanding of electrical safety today can pay dividends in the long run, protecting you and your home from potential hazards. Don't gamble with electricity – educate yourself and be safe.
Unlocking nfl preseason expert picks and predictions
Mastering the art of the humpy fly
Transform your home with the perfect interior wall paint



/ElectricalWiring_FINAL2-5c01dc0546e0fb0001f4d760.png)